BATai: Bias Amplification & Transfer in ai
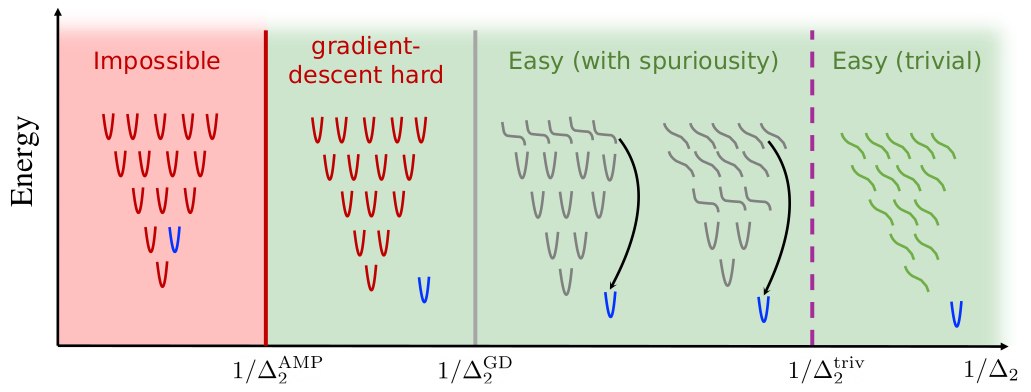
fairnessAs machine learning systems become increasingly pervasive in various aspects of our lives, concerns about the emergence of biases that disproportionately impact vulnerable populations have grown. This issue is of paramount importance, leading governments to take regulatory steps, such as the recent approval of the firsts AI regulations. However, the enactment of such regulations faces significant challenges due to the complex nature of bias generation throughout the machine learning pipeline. This complexity makes it difficult to pinpoint the root causes of bias. Using methods from statistical physics we can understand the fundamental mechanisms that cause bias to be generated and amplified. In this project, I want to understand the implications of supposedly neutral design choices in modern machine learning applications.
LLAMA: LLearning in Animals and MAchines
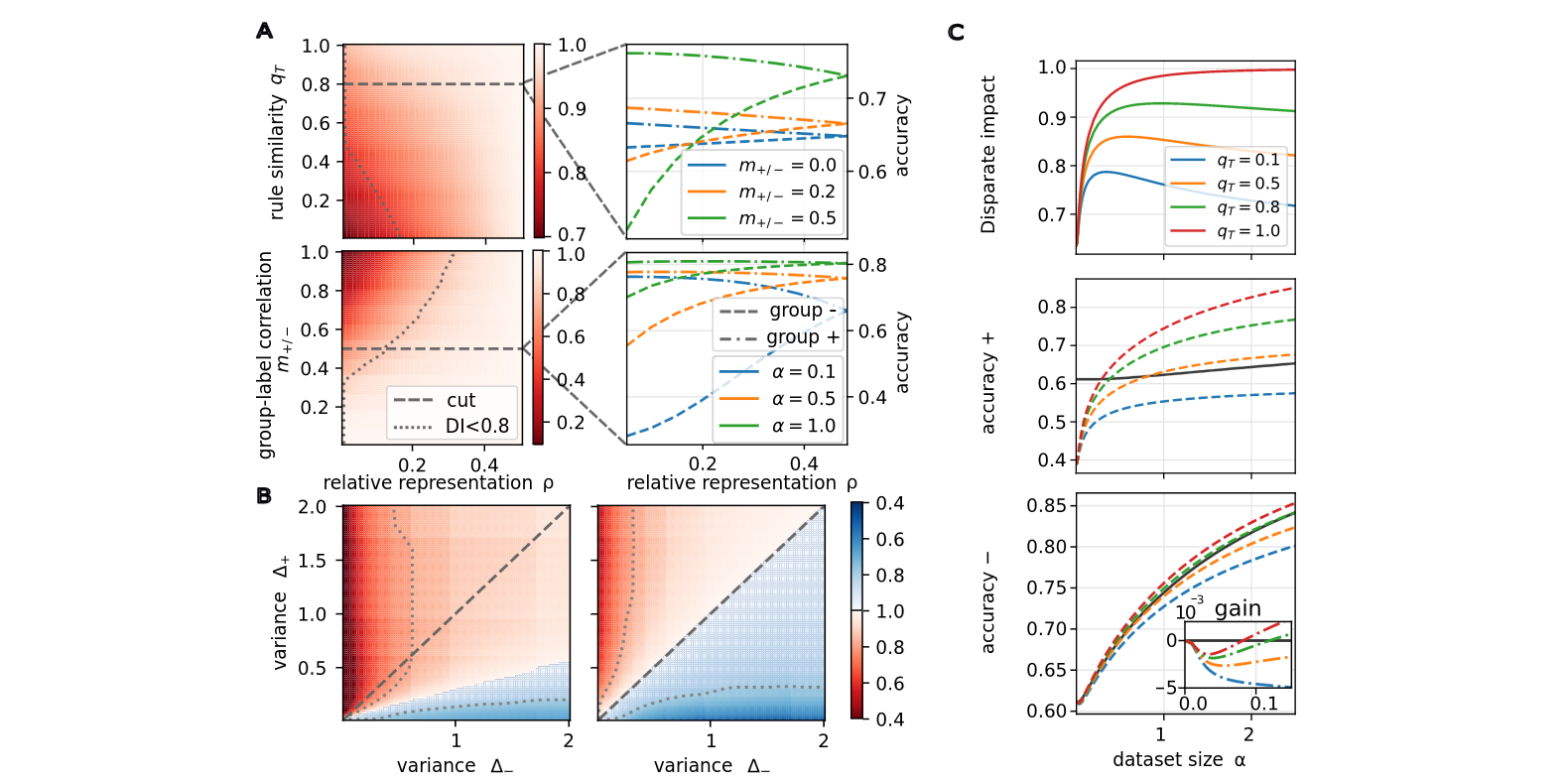
compositionality continual learning curriculum learning reinforcement learning transfer learningArtificial neural networks were originally created to understand the brain mechanistically via a modelling approach. With the breakthrough of deep networks and progress in understanding these algorithms, we now have numerous tools to probe neural networks. Can we use these tools to understand biological neural networks? In particular, this line of research focuses on the discrepancy between how biological and artificial neural networks learn. By understanding the why and how of this difference can lead us to improve modern algorithms and can teach us something about the brain. Several learning mechanisms like continual learning, transfer learning, curriculum learning, and compositional generalisation, are completely natural for animals but pose an astonishing challenge for machines. Why?
BADGER: Bridging Algorithm's Dynamics with GEometRy
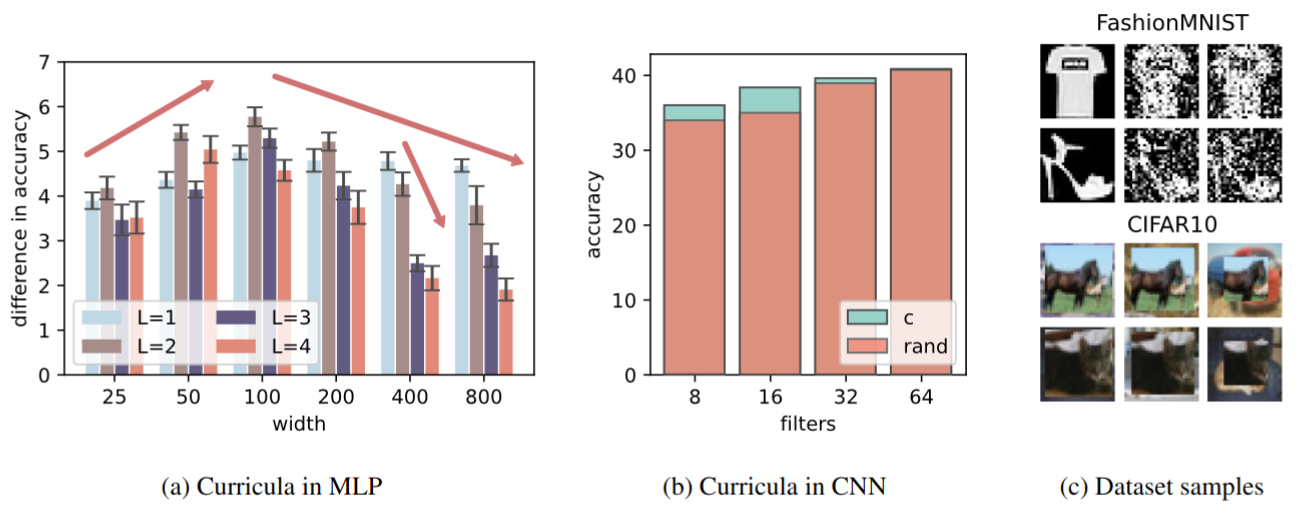
landscape momentum optimisationStarting from a random configuration, to which solution an optimisation algorithm will bring me? This question is perhaps not too complicated in low-dimension, however modern machine learning applications process a huge amount of information and in high-dimension, the same question appears way more challenging. Our intuition in the high-dimensional world is often misleading, and this question found answers in only a few simple cases.